 函数式接口
函数式接口
四大函数式接口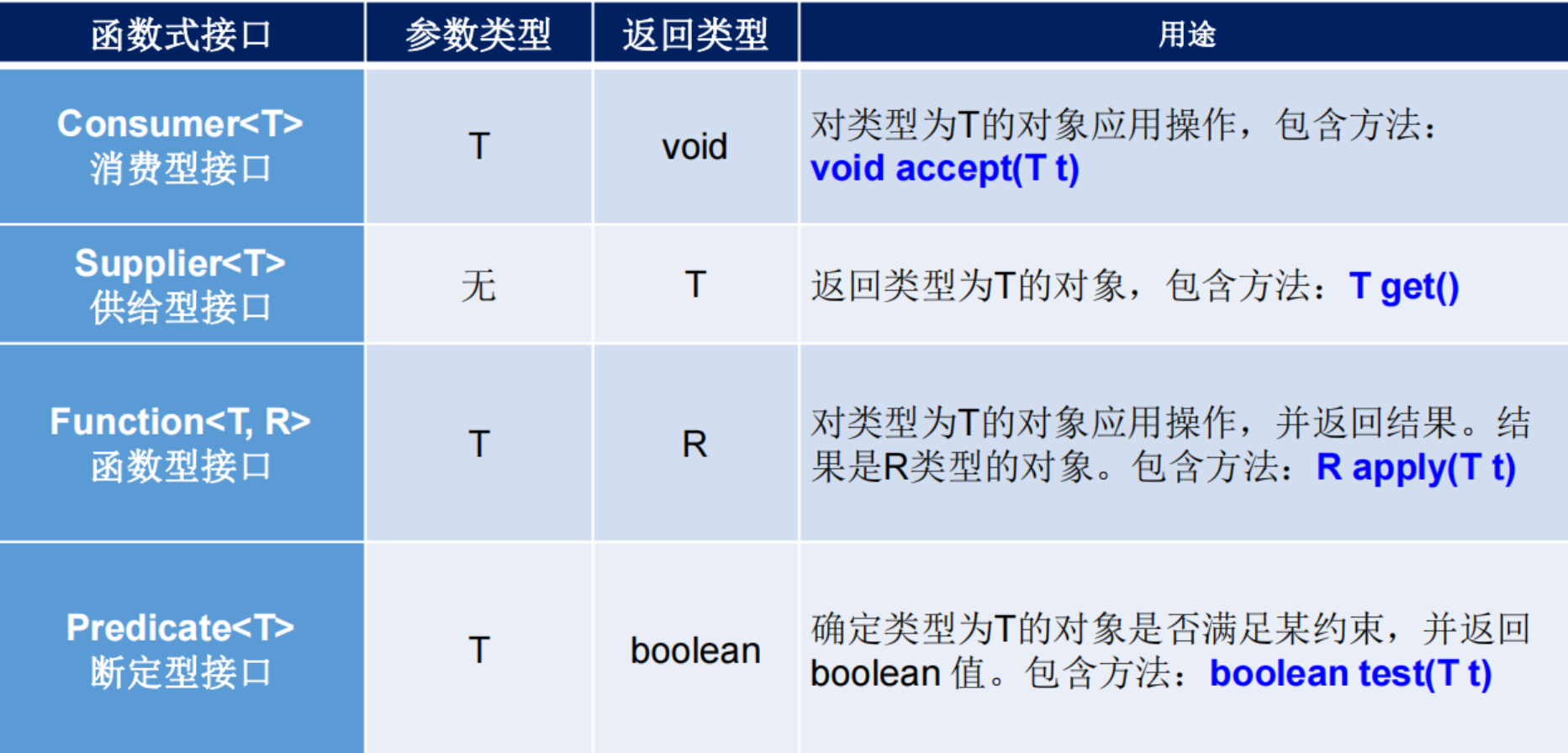
# Consumer
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(1, System.out::println);
}
public static <T> void test(T t, Consumer<T> consumer) {
consumer.accept(t);
}
}
// 打印
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# Supplier
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(test(() -> "test1"));
System.out.println(new MyOptional<>("test2").get());
}
public static class MyOptional<T> implements Supplier<T> {
private final T value;
public MyOptional(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public T get() {
return value;
}
}
public static <T> T test(Supplier<T> supplier) {
return supplier.get();
}
}
// 打印
test1
test2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# Funtion
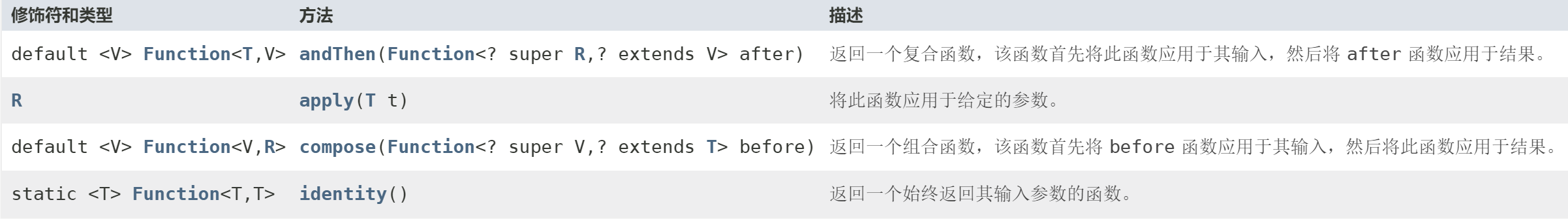
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass myClass = new MyClass("hello");
System.out.println(test(myClass, MyClass::getValue));
}
public static class MyClass {
private final String value;
private MyClass(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
public static <T, R> R test(T t, Function<T ,R> function) {
return function.apply(t);
}
}
// 打印
hello
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
# Predicate
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(test(1, t -> 1 > t));
}
public static <T> boolean test(T t, Predicate<T> predicate) {
return predicate.test(t);
}
}
// 打印
false
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
上次更新: 2023/12/29 11:32:56
